FAQ – FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
We are developing this part of our service, we would like this to be the place you come to for all the answers to your telecommunication questions.
A PBX (private branch exchange) is a telephone system wich provides control over your business lines that are connected from the Telephone Exchange to the business address, generally done over a copper wire a PBX or PABX allows you to control incoming calls which may be placed on hold, transferred to an extension in the business or externally, with many other features.
VoIP technology enables you to make and receive telephone calls over a broadband Internet connection instead of over a traditional phone line.
IP Telephony or Internet Protocol Telephony is the transmission of voice signals over the Internet, wide area network (WAN), or local area network (LAN). IP Telephony uses voice-over-IP to break down voice transmissions into packets of data and transmitting them across a network.
Voice-over-Internet-Protocol or Voice-over-IP or VoIP allows one to send a voice transmission via a network instead of the standard telephone infrastructure. Calls can be routed via the Internet, wide area network (WAN), or local area network (LAN).
With VoIP, voice traffic is converted into data packets and transmitted over the public Internet and/or over a private IP network. When you call a landline or cell phone number, the data packets are converted to a regular telephone signal before they reach the party you’re calling.
For a basic VoIP system, all you need are a broadband Internet connection and a VoIP-enabled phone; a traditional phone connected to an adapter; or a computer with VoIP software.
Many businesses are now using VoIP and unified communications on their own private networks. Telephony systems residing on private networks have better security and quality than those that operate strictly over the public Internet. With VoIP or unified communications on a private network, you can prioritize voice over other types of traffic on your network, to ensure the best possible audio quality.
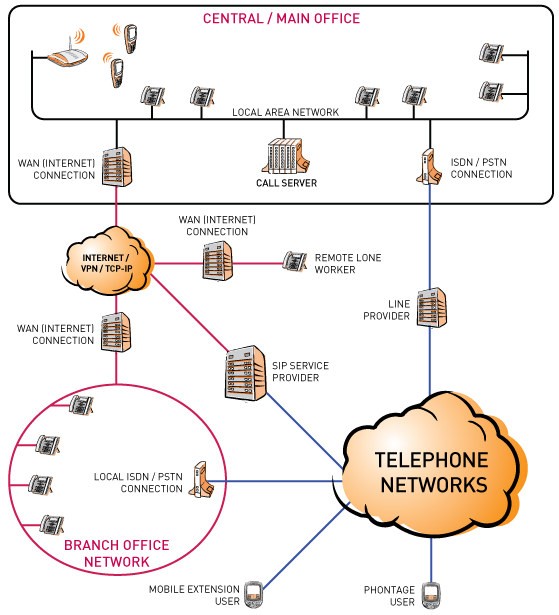
SIP, short for Session Initiation Protocol is an IP telephony signaling protocol used to establish, modify and terminate VOIP telephone calls. SIP was developed by the IETF and published as RFC 3261
SIP describes the communication needed to establish a phone call.
SIP has taken the VOIP world by storm. The protocol resembles the HTTP protocol, is text based, and very open and flexible.
A SIP trunk is a connection between your organization and an Internet Service Provider (ISP). It enables you to extend voice over IP (VoIP) telephony beyond your organisation’s firewall without the need for standard copper wire and a PSTN or ISDN gateway. This is a simpler configuration and it is easier and less expensive to design, operate, maintain, and upgrade. And because ISPs deliver services (notably long distance) at substantial savings, your investment in SIP trunking can give a quick and substantial return on investment.
In addition to VoIP calls via SIP trunks can also carry instant messages, multimedia conferences, user presence information, and other SIP-based, real-time communications services. As SIP-based communication technologies advance and SIP trunking becomes commonplace, additional services are likely to become available.
With all of the benefits that SIP trunking provides (especially the substantial cost savings), it’s no wonder that SIP trunking is a hot topic in unified communications.
You don’t need any particular system, software or hardware to use the Radicall Hosted service. We provide you with a complete system.
You don’t need to keep your existing phone lines to use the Radicall Hosted Service.
Sometimes you might opt to keep at least one of the existing phone lines we can discuss that with you at our discovery interview.
Your ISP is the most important factor in determining call quality – we provide this service and transfer your Internet and WAN services to our network.
We are able to provide ADSL, ADSL2, VDSL2, HSNS and FIBER connections.
Fixed-line based services such as ADSL ADSL2 provide reliable quality for Small Businesses. VDSL provide excellent call quality for Medium Businesses and HSNS or Fiber is recommended for dedicated services where a larger volume of calls is managed.
FAX was designed for analog networks, and does not travel well over a VOIP network. The reason for this is that FAX communication uses the signal in a different way to regular voice communication. When VOIP technologies digitize and compress analog voice communication it is optimized for VOICE and not for FAX. Subsequently, there are a number of things you need to take note of when you move to a VoIP Phone System.
If you want to continue using your old fax machine, and you want to connect to your VoIP phone system, its best to use a VoIP Gateway and an ATA that supports T38. T38 is a protocol designed to allow fax to ‘travel’ over a VoIP network.
It is also possible to convert to computer based fax and choose a VoIP phone system that supports fax.
Another way to deal with fax when you switch to voip are to connect the fax machine directly to the existing analog phone line and bypass your VOIP system.
Yes, we do support Caller ID by number and Caller ID by name.
Unified Communications is defined as the process in which all means of communication, communication devices and media are integrated, allowing users to be in touch with anyone, wherever they are, and in real time.
The objective of Unified Communications is to optimize business procedures and boost human communications by simplifying processes.

